Reinforcement technologies enhances strength, durability, and performance and saving weight.The reinforcement technology is critical for handling high-speed impacts, braking forces, and aerodynamic loads.In a regular rim the manufacturer can’t control the specific stresses by layup only. The spoke force is concentrated around the nipple hole which can result in pulled nipples, broken spokes and a wheel coming out of true when under load.With a pre-defined high modulus reinforcement strip the spoke force is spread out through the reinforced strip and distributes the stresses over a larger part of the rim. The rims are now capable of withstanding a spoke force of more than 300kgf when hand built which offers better wheel performance, durability and reliability.
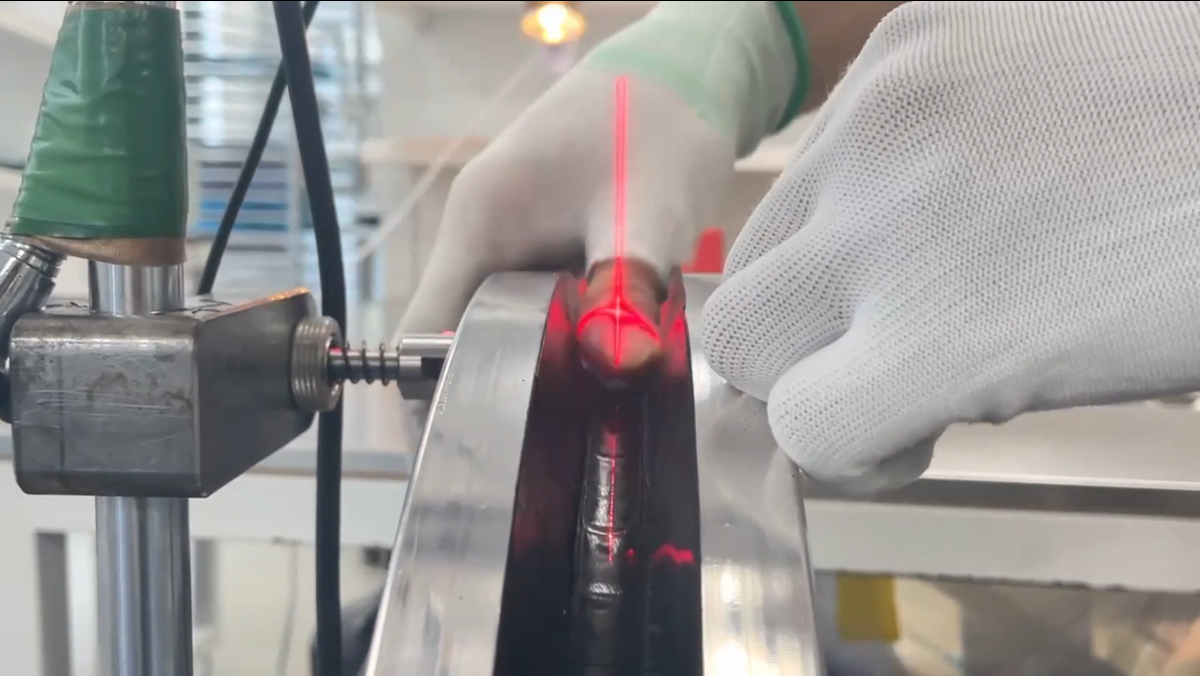
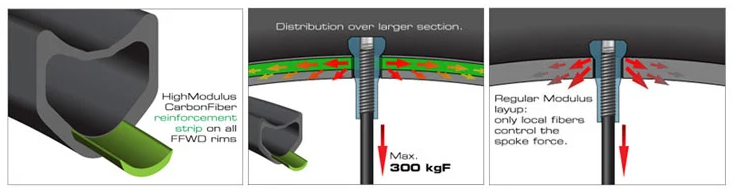
Carbon wheel reinforcement technology at:
Reinforced Rim Beads (Hooked & Hookless).Hooked rims use a lip to lock tires in place.Hookless rims rely on reinforced sidewalls for tubeless setups.
Asymmetric Spoke Lacing.Off-center spoke holes balance tension in disc brake wheels.Prevents wheel flex under braking forces.
Impact-Resistant Layups (Carbon Wheels).Extra carbon layers at the rim bed prevent cracks from rocks/curbs.
Disc brake rims often have asymmetric spoke holes to balance spoke tension.
Future Trends in Bike Reinforcement
3D-Printed Titanium Lattices – Ultra-light, ultra-strong internal structures.
Self-Healing Resins – Microcapsules in carbon fiber that repair small cracks.
AI-Optimized Layups – Computer-designed fiber patterns for perfect stiffness/weight balance.
Which Bike Uses the Best Reinforcement?
Road Bikes: High-modulus carbon with UD layers (e.g., Specialized S-Works, Trek Madone).
MTBs: Hydroformed aluminum + carbon/Kevlar hybrids (e.g., Santa Cruz Carbon CC).
Gravel Bikes: Multi-axial carbon weaves for vibration damping (e.g., Canyon Grail).


